Grow with TuxAcademy
At TuxAcademy, we bridge the gap between education and employment.
Our mission is simple: to make students job-ready with the latest technology skills, hands-on experience, and industry mentorship.
- Artificial Intelligence & Data Science
- Cybersecurity
- Cloud & Blockchain
- Full Stack Development
- Programming (Python, Java, C#, SQL, C, C++)
- Robotics


10+
Online Courses
Top
Instructors
Online
Certifications
10+
Membership
Our Online & Offline
Training Courses
Explore all of our courses and pick your suitable ones to enroll and start learning with us! We ensure that you will never regret it!
Artificial Intelligence
Master AI and build smart systems that shape the future.
Data Science
Turn raw data into powerful business insights with real-world projects.

Cyber Security
Build end-to-end web applications using modern frameworks and tools.

Full Stack Development
Protect IoT devices and their network infrastructure effectively...

Cloud and Blockchain
Gain expertise in scalable cloud solutions and next-gen blockchain technologies.
Programming in Python
Start your coding journey with one of the world's most versatile languages.
Learn & Grow Your Skills From Anywhere
Learn & grow your skills from anywhere with TuxAcademy. Expert trainers, online learning, and lifetime access for all students.
- Expert-Led Training
- Online & Offline Classes
- Real-Time Projects
- Comprehensive curriculum
- Training using industry-grade tools and platforms
Amazing Courses to Learn Better
We understand better that online-based learning can make a significant change to reach students from all over the world! Giving options to learn better always can offer the best outcomes!
- Skilled Teachers
- Affordable Courses
- Efficient & Flexible
- Lifetime Access



What Our Students Have To Say
Hear from our students! Discover how our courses and expert trainers have helped learners gain practical skills and advance their careers.

TuxAcademy is a place to learn AI and other modern technologies. I took AI training in this institute and using same in Job. AI program by TuxAcademy helped me in career growth.
Gautam

I can't say enough good things about Tux Academy! From the moment I enrolled, I was impressed by the professionalism, expertise, and passion of the instructors. The curriculum is thorough...
Hemant Vats

TuxAcademy head office where toppers get real world project exposure and do research on specific areas.
Vaibhav kushwaha

TuxAcademy is a premier learning hub for Ethical Hacking, Robotics, IoT, Cyber Security, AI, and Software Development. Guided by "Keep Learning, Keep Growing," it offers expert mentorship
Abhishek
Course Instructors
Geetanjali Mehra
AI & Data ScienceShekhar Kumar
Cyber SecurityMohit Panwar
Full Stack DevelopmentSidharth
Programming & RoboticsOur Placements
At TuxAcademy, we take pride in shaping careers and building industry-ready professionals. Proudly placed our students with leading companies and growing every day.







Get News with TuxAcademy
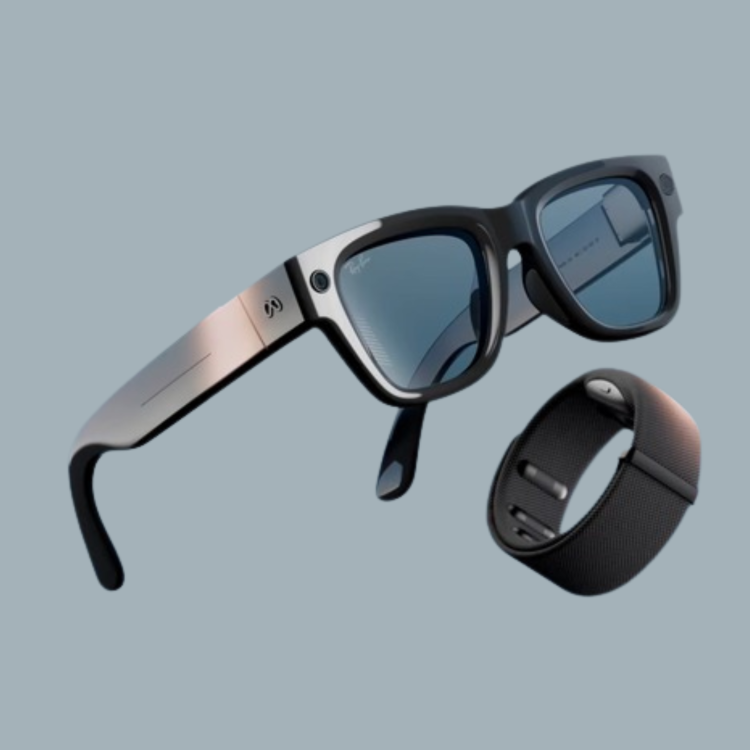
Meta unveiled Ray-Ban
- 28 Sep, 2025
- Com 0
Meta unveiled Ray-Ban AI-powered display glasses featuring a built-in display that can be controlled using muscle movements through...
AI Impact Summit
- 28 Sep, 2025
- Com 0
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has selected eight new organisations...